Last Updated on July 27, 2023
Throughout history, women have faced numerous challenges and barriers in the workplace, including the issue of unequal pay. The struggle for equal pay has been a long and arduous one, with women fighting for their rights and fair treatment. This article will explore the historical context of gender inequality in the workplace, the early efforts towards achieving equal pay for women, and the impact of the Equal Pay Act of 1963. It will also discuss the challenges and setbacks faced in the fight for equal pay, the role of women’s rights movements in advancing pay equality, and the legislative measures and policies promoting pay equity. Additionally, it will highlight the progress made in recent years towards closing the gender pay gap, while acknowledging the ongoing barriers and the need for continued advocacy. By examining the past and present, we can gain a better understanding of when women truly achieved equal pay and the work that still needs to be done.
Historical context of gender inequality in the workplace
Gender inequality in the workplace has a long and complex history, with women facing numerous challenges and barriers to achieving equal pay. Here are some key points to consider:
- Throughout history, women have been traditionally assigned to domestic roles, while men have dominated the workforce.
- Women were often paid significantly less than men for doing the same job, with their work undervalued and dismissed.
- Discrimination and stereotypes about women’s abilities and roles in society further perpetuated gender inequality in the workplace.
- Women were often excluded from higher-paying professions and faced limited opportunities for career advancement.
- Even when women did enter the workforce, they were often confined to low-paying jobs with little room for growth.
These historical factors laid the foundation for the gender pay gap and set the stage for the fight for equal pay.
Early efforts towards achieving equal pay for women
Throughout history, women have faced significant challenges in the workplace, including unequal pay for equal work. However, there have been early efforts to address this issue and strive for pay equality. One such effort was the formation of women’s labor organizations in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. These organizations fought for fair wages and better working conditions for women.
Another important milestone in the pursuit of equal pay was the establishment of the National Women’s Trade Union League in 1903. This organization played a crucial role in advocating for women’s rights in the workplace, including equal pay. They organized strikes and protests, lobbied for legislative changes, and raised awareness about the issue of unequal pay.
Despite these early efforts, achieving equal pay for women remained a long and arduous journey. It wasn’t until the passage of the Equal Pay Act of 1963 that significant progress was made in addressing the gender pay gap. This landmark legislation prohibited wage discrimination based on sex and paved the way for future advancements in pay equality.
The Impact of the Equal Pay Act of 1963
The Equal Pay Act of 1963 was a landmark legislation that had a significant impact on the fight for gender equality in the workplace. This act, signed into law by President John F. Kennedy, aimed to address the wage gap between men and women by prohibiting employers from paying women less than men for equal work.
Prior to the enactment of the Equal Pay Act, women faced widespread discrimination in terms of wages and job opportunities. They were often paid significantly less than their male counterparts, even when performing the same job with the same level of skill and experience. This inequality not only affected women’s financial well-being but also perpetuated gender stereotypes and limited their career prospects.
The Equal Pay Act sought to rectify this injustice by establishing the principle of equal pay for equal work. It mandated that employers provide equal pay to employees of both sexes who perform substantially similar work, regardless of their gender. This legislation was a crucial step towards achieving pay equity and challenging the systemic gender discrimination that had long been ingrained in the workplace.
Challenges and setbacks in the fight for equal pay:
– Despite the passing of the Equal Pay Act in 1963, achieving equal pay for women has been an ongoing struggle.
– One of the main challenges has been the persistence of gender stereotypes and biases that undervalue women’s work.
– Women continue to face discrimination in hiring, promotion, and salary negotiations, which contributes to the gender pay gap.
– The gender pay gap is also influenced by occupational segregation, with women being overrepresented in lower-paying industries and professions.
– Another setback is the lack of transparency in pay practices, making it difficult for women to identify and challenge pay disparities.
– Women of color face even greater challenges in achieving pay equity, as they experience both gender and racial discrimination in the workplace.
– The gender pay gap is further exacerbated by the motherhood penalty, where women’s earnings decrease after having children.
– Legal loopholes and inadequate enforcement of equal pay laws have also hindered progress in closing the gender pay gap.
– The fight for equal pay requires ongoing advocacy and awareness to address these challenges and ensure that women receive fair and equal compensation for their work.
The Role of Women’s Rights Movements in Advancing Pay Equality
Throughout history, women have faced significant challenges in achieving equal pay in the workplace. However, the tireless efforts of women’s rights movements have played a crucial role in advancing pay equality. Here are some key points to consider:
- Women’s rights movements, such as the suffrage movement in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, laid the foundation for advocating for equal pay.
- These movements fought for women’s rights to education, employment, and fair wages, highlighting the importance of economic independence for women.
- The feminist movement of the 1960s and 1970s further pushed for equal pay, challenging societal norms and demanding equal opportunities for women in the workforce.
- These movements raised awareness about the gender pay gap and the need for legislative action to address this issue.
- Through protests, demonstrations, and lobbying efforts, women’s rights movements pressured lawmakers to enact laws and policies aimed at achieving pay equality.
- These movements also played a crucial role in changing societal attitudes towards women in the workplace, challenging stereotypes and promoting gender equality.
Overall, women’s rights movements have been instrumental in advancing pay equality by raising awareness, advocating for legislative measures, and challenging societal norms. However, the fight for equal pay is far from over, and continued advocacy is needed to overcome ongoing barriers and achieve true pay equity.
Legislative measures and policies promoting pay equity
Over the years, various legislative measures and policies have been implemented to promote pay equity and address the gender pay gap. These initiatives aim to ensure that women receive equal pay for equal work, and to eliminate discrimination based on gender in the workplace.
One significant legislative milestone in this regard was the Equal Pay Act of 1963. This federal law made it illegal to pay men and women different wages for performing substantially equal work. It was a crucial step towards achieving pay equality and combating gender-based wage discrimination.
In addition to the Equal Pay Act, other laws and policies have been enacted at both the federal and state levels to promote pay equity. These include the Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act of 2009, which extended the time period for filing pay discrimination claims, and various state laws that prohibit employers from asking job applicants about their salary history.
Furthermore, some companies and organizations have voluntarily implemented policies to promote pay equity. This includes conducting regular pay audits, implementing transparent pay scales, and providing training on unconscious bias and gender equality in the workplace.
While these legislative measures and policies have made significant strides towards closing the gender pay gap, there is still work to be done. Ongoing advocacy and continued efforts are necessary to ensure that pay equity becomes a reality for all women in the workforce.
Progress made in recent years towards closing the gender pay gap
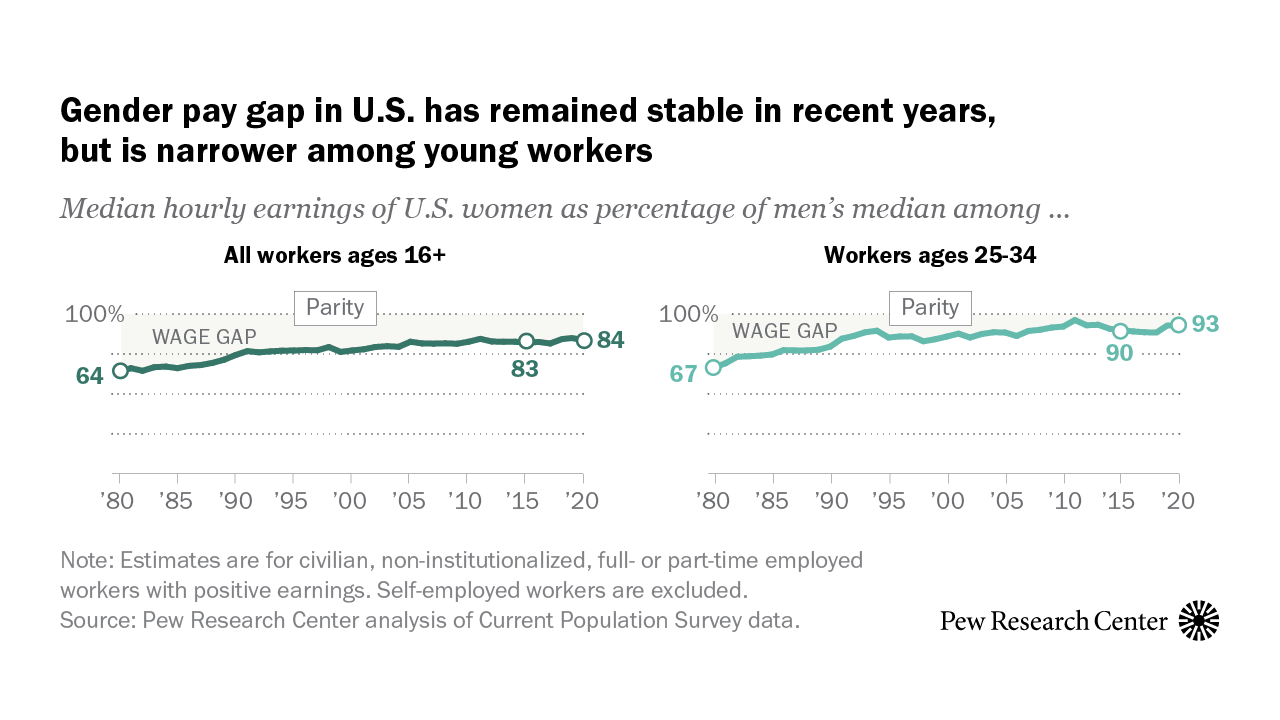
In recent years, there has been significant progress towards closing the gender pay gap. Organizations and governments have recognized the importance of pay equity and have taken steps to address this issue. One key development is the implementation of pay transparency measures, which require companies to disclose salary information to employees. This allows individuals to compare their salaries with their colleagues and identify any discrepancies based on gender. Additionally, many companies have implemented diversity and inclusion initiatives, aiming to create a more equitable workplace. These initiatives include unconscious bias training, mentorship programs, and flexible work arrangements. Furthermore, some countries have introduced legislation to enforce pay equity. For example, Iceland became the first country to require companies to prove that they are paying men and women equally. While progress has been made, there is still work to be done. The gender pay gap persists, particularly for women of color and those in low-wage jobs. Continued advocacy and awareness are crucial to ensure that equal pay becomes a reality for all women.
Ongoing barriers and the need for continued advocacy
Despite the progress made in recent years towards closing the gender pay gap, there are still ongoing barriers that prevent women from achieving equal pay. One of the main barriers is the persistence of gender stereotypes and biases in the workplace. These stereotypes often lead to women being undervalued and underpaid for their work, especially in male-dominated industries.
Another barrier is the lack of transparency in pay practices. Many companies do not openly disclose salary information, making it difficult for women to know if they are being paid fairly compared to their male counterparts. This lack of transparency also makes it harder for women to negotiate for higher salaries.
Additionally, women continue to face challenges in balancing work and family responsibilities. The gender pay gap widens for women who take time off to care for children or elderly family members, as they often face reduced opportunities for career advancement and lower wages upon returning to work.
To address these ongoing barriers, continued advocacy is crucial. Women’s rights organizations and activists must continue to push for policies that promote pay equity, such as stronger equal pay laws and increased transparency in pay practices. Employers also have a role to play in implementing fair pay policies and addressing gender biases in the workplace.
Ultimately, achieving equal pay for women requires a collective effort from individuals, organizations, and policymakers. By working together, we can create a more equitable and inclusive society where women are valued and compensated fairly for their contributions.
Conclusion: The journey towards achieving equal pay for women has been a long and arduous one, marked by both progress and setbacks. From the early efforts towards pay equality to the enactment of the Equal Pay Act of 1963, significant strides have been made in addressing gender inequality in the workplace. Women’s rights movements have played a crucial role in advancing pay equality, pushing for legislative measures and policies that promote pay equity. While progress has been made in recent years towards closing the gender pay gap, there are still ongoing barriers that need to be addressed. Continued advocacy is necessary to ensure that women receive the same compensation as their male counterparts for equal work. It is imperative that we continue to fight for pay equality, not only for the sake of fairness and justice, but also for the economic empowerment of women and the overall well-being of society.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the fight for equal pay for women has been a long and challenging battle. Throughout history, women have faced significant gender inequality in the workplace, but early efforts towards achieving pay equality paved the way for progress. The enactment of the Equal Pay Act of 1963 was a major milestone in addressing this issue, but challenges and setbacks have persisted. Women’s rights movements have played a crucial role in advancing pay equality, advocating for legislative measures and policies that promote fair compensation. While progress has been made in recent years towards closing the gender pay gap, there are still ongoing barriers that need to be overcome. Continued advocacy and awareness are essential to ensure that women receive the same pay as their male counterparts for equal work. Achieving pay equality is not only a matter of fairness, but also a crucial step towards empowering women and creating a more equitable society.
Discover the historical context, challenges, and progress made in achieving equal pay for women in this informative article.
About The Author

Alison Sowle is the typical tv guru. With a social media evangelist background, she knows how to get her message out there. However, she's also an introvert at heart and loves nothing more than writing for hours on end. She's a passionate creator who takes great joy in learning about new cultures - especially when it comes to beer!