Last Updated on September 16, 2022
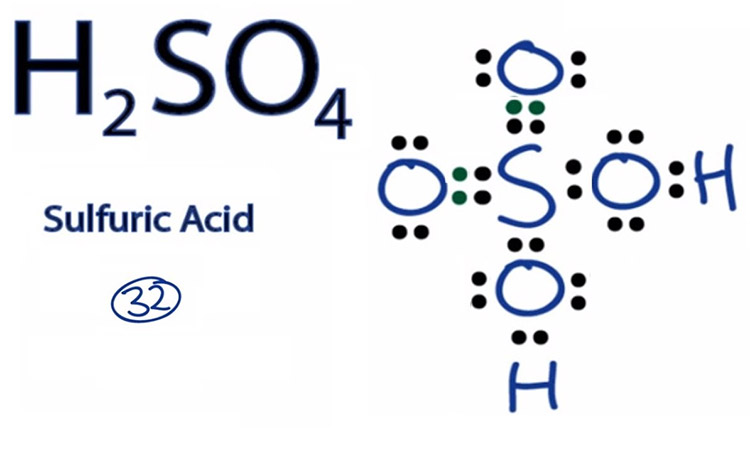
H2SO4 is a common chemical compound, consisting of two hydrogen atoms, one sulfer atom, and four oxygen atoms. This substance is a strong acid, soluble in water, and highly polar, making it an excellent solvent. It is used in fertilizer and detergent production. This article discusses the properties and uses of sulphuric acid.
sulphuric acid
Sulphuric acid, H2SO4, is an inorganic chemical with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is soluble in water in all concentrations, and separates into two negatively-charged ions, sulfate and hydronium, upon contact with a solvent. The concentration of sulfuric acid in an aqueous solution is expressed in molarity, which indicates the number of ions per liter of the solution.
Sulphuric acid is toxic when it comes into contact with the skin, eyes, and lungs. The International Agency for Research on Cancer and the ACGIH have classified strong sulfuric acid mists as a type of carcinogen. But these chemicals are different than liquid sulfuric acid, which is a neutral aqueous solution. To find out how toxic sulfuric acid is to humans, consult Table 6.20.
Sulfuric acid is a colorless, odorless, and highly miscible with water. The pure chemical, H2SO4, does not exist in the earth’s atmosphere. However, its concentration is highly corrosive and readily absorbs water vapor from the air. Although it is colorless and odorless, H2SO4 is highly corrosive, the chemical’s dehydration process converts it to the non-corrosive sulfur trioxide.
The preparation of sulfuric acid is hazardous due to the heat generated during the process. To make a solution of sulphuric acid, a concentrated solution of H2SO4 is mixed with water. Water’s high heat capacity allows sulfuric acid to boil, so if it is too concentrated, it could explode. Typically, the highest concentration of sulfuric acid is six M (30%), and solutions over six M (30%) are the most dangerous. Furthermore, as the acid concentration increases, the reaction rate doubles. Therefore, if you plan to dilute the acid, it’s best to use external cooling and efficient mechanical stirring.
Diluted sulfuric acid reacts with a variety of metals via single displacement reactions, forming hydrogen gas and a metal sulfate. Iron, zinc, and manganese are all susceptible to sulfuric acid, while copper and lead are more resistant. In some cases, sulfuric acid is a byproduct of the oxidation of sulfur dioxide, which is produced during the combustion of fuels containing sulfur.
Sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide is also known as nisso sulfan and has a compound formula of SO3. It is the most important economically important sulfur oxide, and is produced on a large scale as a precursor for sulfuric acid. This article provides an overview of the properties of sulfur trioxide. It is a toxic gas. To keep your home free of it, you should avoid it.
Sulfur trioxide is a highly reactive compound. It is composed of two hydrogen atoms, one sulfer atom, and four oxygen atoms. This acid is extremely polar, making it an excellent solvent. It is also used in the production of fertilizers and detergents. While its chemical composition is quite complex, it is relatively easy to understand.
The spectrum of aqueous sulfuric acid varies with the protonation state of the acid molecule. This change is due to differences in valence orbitals, which chemically bind protons. Acid molecules with one or two protons exhibit the lowest Kbx emission line. The averaged spectra of the three forms are shown in Fig. 3(e). The Kbx and Kb” features can be detected on the S-type spectrum of H2SO4.
Sulfuric acid is extremely corrosive to human tissue and should be flushed with warm water after contact. Unlike alkalis, it is not neutralized by water, so it is not a good idea to mix diluted sulfuric acid with a corrosive substance. This is because alkalis can neutralize the chemical on work surfaces and floors, but should not be used on human internal tissues. If you accidentally come into contact with sulfuric acid, seek medical attention.
The most common sources of sulfur are fossil fuels, such as unrefined petroleum and natural gas. Mineral ores are also sources of sulfur. Sulfur dioxide is converted to sulfur trioxide by a process known as pyrolysis. The fuming sulfuric acid is then added to the hydrogen pyruvate to make more sulfur. Aqueous sulfuric acid is produced as a result of this process.
Sulfuric acid as a catalyst
Sulfuric acid is a common industrial chemical used to produce a variety of chemical products. In the chemical industry, it is often used as a catalyst for the production of hydrochloric acid from salt. In the petroleum refining process, it is used to make cyclohexanoneoxime, a precursor to nylon. In dyestuffs, sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst in the conversion of starch and carbon.
The acid has a catalytic effect on the hydration of 1-methanethio-2-phenylethyne. This reaction is similar to the hydration of arylalkyl thioacetylenes catalyzed by the mercuric ion. However, the mercuric ion is much stronger than the phenyl.
In the case of aqueous solutions, a small amount of sulfuric acid can be added to white sugar to make a dark column of porous carbon. The solution is likely to smell strongly of caramel, as it combines with the sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is a powerful antioxidant and may also act as a chelating agent for heavy metals.
Sulfuric acid has the potential to cause severe chemical burns and secondary thermal burns. It is therefore crucial to use adequate safety precautions when handling it. It is important to remember that solutions that contain more than six M (30%) are the most toxic. As the concentration of the acid increases, the rate of reaction increases twofold. Thus, when preparing an acid solution, it is necessary to ensure efficient mechanical stirring during the entire process.
Sulfuric acid is usually mixed with hydrogen peroxide in a 3:1 to 7:1 ratio. It is useful for removing trace amounts of organic residues from substrates. Hydrogen peroxide reacts vigorously with concentrated sulfuric acid to produce highly activated peroxymonosulfuric acid, also known as Caro’s acid. However, caution should be exercised when handling sulfuric acid because it can cause explosive reactions if it is mixed with water.
Sulfuric acid is produced by the burning of sulphur in the presence of air. Sulphur dioxide is then converted to sulphur trioxide by the use of a vanadium pentoxide catalyst. The remaining concentrated sulphuric acid is reprocessed. Its waste contains vanadium and arsenic, so care must be exercised when disposal into a landfill.
Sulfuric acid as a basic raw material
Sulfuric acid is a diprotic acid, with a much higher acid-dissociation equilibrium constant than many common acids. Its ph in a strong solution is extremely low, and it can be toxic. However, its many other properties make it an excellent chemical raw material. This article will discuss the various uses of sulfuric acid.
Sulfuric acid is a highly important commodity chemical. The amount of sulfuric acid produced reflects a nation’s industrial strength. Although it is most commonly used in fertilizer production, it also has numerous uses in wastewater treatment, petroleum refining, mineral processing, and chemical synthesis. Sulfuric acid has a wide range of industrial applications, including metallurgical, food, and pharmaceutical industries.
Sulfuric acid is a valuable chemical, and its dehydrating properties make it a useful compound for fertiliser production. One of the most important fertilisers for acidic soils is lime superphosphate. Another popular fertiliser is ammonium sulphate, which neutralizes alkaline soils and creates mild acidic conditions in soil.
Sulfuric acid is also used for iron and steel production. In the steel industry, sulfuric acid is used as a pickling-acid to remove oxidation, rust, and scale from steel. It is also sold to manufacturers of white goods and automobiles. In addition to its industrial uses, sulfuric acid is recycled through Spent Acid Regeneration plants. In these facilities, the spent acid is burned with fuel to create sulfur trioxide and gaseous sulfur dioxide. These two products are then used to make new sulfuric acid.
Due to its high affinity for water, sulfuric acid is a highly hazardous substance. Its high dissociation constant, which causes the first hydrogen to be released during reactions, makes sulfuric acid a strong oxidizer. In addition to being hazardous to human health, sulfuric acid also burns paper and human skin. Sulfuric acid is highly corrosive and can pose a significant safety hazard in high concentrations.
Sulfuric acid is produced in massive quantities on a global scale, and its production is directly tied to a country’s development. It is used in a range of industrial processes, including inorganic pigment manufacturing, copper leaching, petroleum refining, and paper production. The main problem with sulfuric acid is that it is toxic when mixed with other chemicals or water, and it should always be diluted with water before use.
About The Author

Zeph Grant is a music fanatic. He loves all types of genres and can often be found discussing the latest album releases with friends. Zeph is also a hardcore content creator, always working on new projects in his spare time. He's an amateur food nerd, and loves knowing all sorts of random facts about food. When it comes to coffee, he's something of an expert - he knows all the best places to get a good cup of joe in town.