Did you know that Egyptians built their homes around the Nile River? They sand-filled the riverbank and used papyrus reeds. However, over time, these homes were washed away due to the river’s strong currents. This is when they developed the idea of making bricks out of mud. This brick material was stronger than plain mud and allowed the Egyptians to build taller walls. They also learned how to build their homes in a way that allowed the wind to cool them.
What was built around the Nile River?
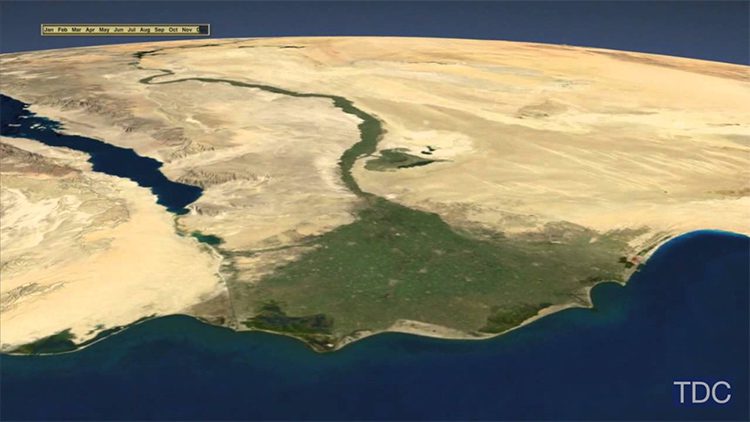
Ancient Egypt was surrounded by a river – the Nile – that gave the people of the region water, fertile soil, and transportation of building materials. The Nile transformed the area into an oasis a few thousand years ago, and today, it remains one of the largest waterways in the world, with more than 6,600 km of navigable water. Families gather water on the banks of the river today, often against the backdrop of ancient Egyptian ruins.
The Nile’s original course was far different from the current one. The river used to bypass Egypt and flow through Libya to the Gulf of Sidra. However, during the last ice age, sea levels rearranged its course. The Nile has been a lifeline for humans for thousands of years, and its banks are home to diverse wildlife, including the legendary Nile crocodile. Here, you can explore the history of the Nile, and learn more about life along the river.
What is the delta area of the Nile river?
The delta is an area in Egypt that lies south of the Nile river. This delta area is comprised of substantial urban neighbourhoods in coastal governorates and stretches between Alexandria and Port Said. The delta receives between 100 and 200 mm (4 to 8 inches) of rainfall per year, with most of the rain occurring in the winter months. It is also the site of the largest inland delta in the world, with a delta area of approximately 1,600 sq km (300 square miles).
The Nile is formed from the blending of three main sources. The White Nile originates at a spring in BURUNDI, flows north through northern UGANDA, and then plunges over a waterfall in the north. The Nile then wanders north through the sudd swamps of southern SUDAN. As its course becomes more northerly, the escarpments on both sides of the river begin to diminish and the Nile widens.
What is the Nile river delta known for?
Ancient ruins are not the only attractions of the Nile river delta. Its most prominent attraction is the ruins of the ancient Egyptian city of Tanis. Built on the historic distributary of the River Nile, this city served as the capital of the 21st and 22nd dynasties during the Third Intermediate Period. It was inhabited until the Roman era, but the port had sunk during the Roman period. Archeologists from France first excavated the abandoned city in the 19th century.
In the fall, parts of the Nile river are red with lotus flowers. The Lower Nile is home to Egyptian lotus, while the Upper Nile is home to Cyperus papyrus, which is fast becoming endangered. Many water birds migrate to the delta for the winter, including several hundred thousand terns. It is home to the world’s largest concentration of little gulls and whiskered terns. Other resident birds include ibises and cormorants.
How did deserts help Egyptians?
Deserts in Egypt are a fascinating topic. While most people associate deserts with lifeless matters, deserts are often more beautiful than people think. The desert has lured countless travelers from the safety of their homes in search of knowledge, adventure, and a taste of eternity. Like the pharaohs of old, the Egyptians were no strangers to the desert. The desert possesses many identities, offering an intensity of meaning that can be quite challenging to describe. But if you take the time to explore this place, you’ll find that you’ll be rewarded with a renewed sense of self.
The ancient Egyptians relied on the deserts to sustain their civilization. The annual flooding of the Nile River provided extremely fertile land for farming and other agricultural activities. The fertile oases of the Western Desert were also key resources for ambitious pharaohs, and the ancient Egyptians exploited these rich areas to expand their civilization. It also provided the Egyptians with precious metals and semi-precious stones.
How did Egypt build their homes?
How did the Ancient Egyptians build their homes? Ancient Egyptians would build their houses out of bricks, which are made from mud. Mud bricks were plentiful because of the annual flood. The brick makers would combine mud and straw with water and mix them together. After mixing the mud and straw, they would shape the mud into bricks, which were then stacked and dried. The walls of wealthy houses were doubled in thickness to provide extra security. Unlike today, poor homes were usually only one brick thick.
The mud brick houses were cheap to build, but they lasted only for a few years. The houses had windows and doors made from reeds, which were used as window coverings. They also provided shade and kept out the dust. Ancient Egyptians also built their homes with mud and straw. The walls of these homes were one block thick and could be made into bricks after drying. The roofs were usually flat, and the interior contained a reed canopy for shade.
What is the Nile Delta made of?
The Nile Delta region of Egypt lies in the great desert belt. The temperatures in Cairo can reach 12 degrees Celsius in January and 31 degrees in July. It does not receive much rainfall, and most of its hazardous waste is produced by industrial operations and chemical plants. Water pollution in the delta also results from sewage, agricultural pesticides, and industrial activities. Despite these challenges, the Nile remains a major trade route and an important part of life in the region.
Ancient Egyptians used the river for recreational purposes. Canoes with two men in them were used for jousting matches. The rower controlled the orientation of the boat and the other was the fighter’s opponent. The river serves as one of the most important bird migration routes in the world, with millions of birds passing through the area each year. As a result of all this, the delta’s water resources are vital to the economic development of Egypt.
How do you make ancient Egyptian houses?
To build an Ancient Egyptian house, you will need to learn how to use natural materials to create your own structure. In the past, Egyptians built their homes with mud or reeds. Then, they filled a brick mold with the mixture. Because wood was scarce in Ancient Egypt, the Egyptians had to import it. They also slept on mattresses on the floor. You can create a realistic Ancient Egyptian house by using a small box, which can be turned inside out to paint and folded flat so you can work on it.
Wealthy Egyptians constructed their homes using stone, and they had gates made of granite to protect them from the elements. The houses were large and usually had many rooms. The rich had their homes painted white to reflect the heat and sun. They also had bathrooms, although there was no running water. The interior walls were often painted pastel colors, to give them a fresh, clean look. Poorer Egyptians usually used just one layer of mud-brick, while richer Egyptians used two or three layers.
What is the land around the Nile Delta known as?
The area surrounding the Nile Delta is home to many ancient sites. The largest of these is the Tanis settlement, which was established on an historic distributary of the Nile River and was probably the capital of the 18th nome of Lower Egypt. The site has been the location of numerous archaeological finds, and even the famous Rosetta Stone was discovered there in 1799. In fact, the name is a anglicized version of the Arabic word “Rashid,” which means “king”.
The Nile Delta is a densely cultivated piece of land that covers about six million acres and is characterized by canals and fields. It is dotted with papyrus and hyciths and is a significant source of fertilizer and food for Egypt. In total, the area has around six million acres of arable land, and is a prime example of how a river can affect an entire region.
About The Author

Wendy Lee is a pop culture ninja who knows all the latest trends and gossip. She's also an animal lover, and will be friends with any creature that crosses her path. Wendy is an expert writer and can tackle any subject with ease. But most of all, she loves to travel - and she's not afraid to evangelize about it to anyone who'll listen! Wendy enjoys all kinds of Asian food and cultures, and she considers herself a bit of a ninja when it comes to eating spicy foods.