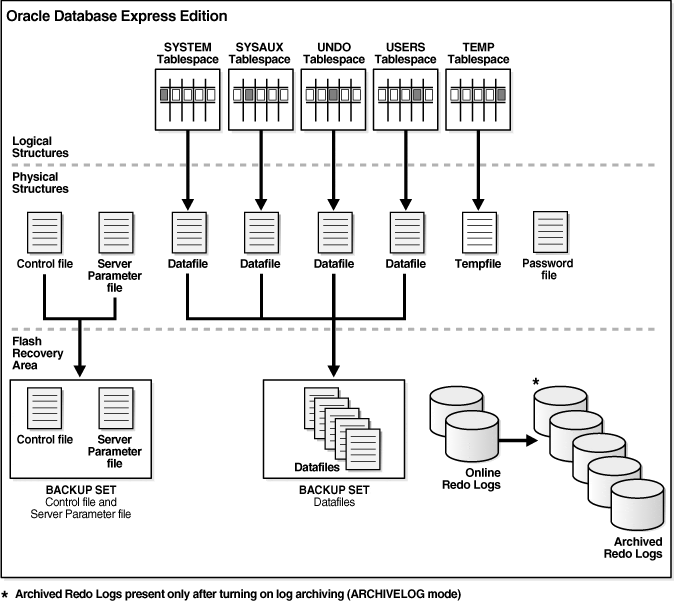
To reclaim flash recovery area space, delete any files, transient files, and system archived logs that are taking up space. To do this, use the V$Flash_Recovery_Area_Usage View. If you need more space, you can also delete the archive log to free up additional space. However, these methods may not work for all applications. If you are unsure which one to delete, refer to this article for help.
Delete files from the flash recovery area
You can run RMAN maintenance to delete unnecessary backups. However, if you’re using an off-site storage device, you may want to keep backups on a local hard disk as well. If the disk space in the recovery area is full, you can use RMAN to force the deletion of backups. The RMAN CROSSCHECK command identifies backups that have expired. When a backup reaches the expiry date, RMAN will delete it automatically.
Performing backups on a regular basis will help you maintain a healthy and secure data storage environment. However, you may need to run backups frequently or run a full test on your database to determine how much space is available. It’s also possible that you run out of space in the flash recovery area, so it’s important to monitor its availability. If you have a limited storage space, you can set a parameter to specify the amount of space allocated to the recovery area. You should set this parameter to a small amount of space, so it does not exceed the total amount of disk space available. If you reach this limit, your backups will fail.
Backups from the flash recovery area are stored in tertiary storage. However, once these backups have been transferred to tape, you can delete them and transfer them to tertiary storage. If you want to move the backups to another location, you can use the BACKUP RECOVERY AREA command. The command BACKUP RECOVERY AREA will back up all recovery area files to a tape.
In addition to archived redo log files, the database may also delete backups from the flash recovery area. This strategy will free up disk space and is useful if half of your data blocks change in the interval between backups. When you’re doing a full database backup, you should use this strategy if you need to delete a large number of files. But, it’s not the only way to keep backups.
Another way to delete files from the flash recovery area is by backing up the data in tertiary storage. You can use the BACKUP RECOVERY AREA to backup files to media manager. The TERTIARY storage option will make your files eligible for deletion. It’s a great way to avoid losing important data. So, how do you delete files from the flash recovery area? Once you know which steps you need to take, you’ll be able to delete files from the flash recovery area.
First of all, you must configure the retention policy for the files in the flash recovery area. You can do this using the RMAN configure retention policy command. If your storage area is not full, you can choose to delete files from this area as long as there’s enough space to accommodate new ones. Besides that, it’s also possible to move these files to the new flash recovery area using standard file-moving procedures.
Delete transient files from the flash recovery area
You can manually delete transient files from the flash recovery area space if they no longer serve any useful purpose. For example, deleting a database backup can help to clear up space on your hard drive. You can delete files listed in Table 5-2 and move the backup to another storage media such as tape. But before you go and delete transient files from the flash recovery area, make sure you have the space available for new ones.
You should not disable the retention policy unless you want your database to have more space. This is because the flash recovery area will be fully used if you don’t delete your files. This will cause the database to behave as if it is full. And you shouldn’t forget that the recovery area space interferes with the normal operation of your database. That’s why you need to make frequent backups of the recovery area space to avoid this issue.
However, you can manually delete these files from the flash recovery area space as long as you have the appropriate privileges. By default, the archived redo logs are automatically deleted once they are no longer needed. This option is also available for users who don’t want their backups to be overwritten. However, this method is not recommended for production environments. To safely manage the flash recovery area space, you should configure the retention policy and the archived log deletion policy.
A flash recovery area file is typically quite large. Operating system file caching is ineffective for large database files, which will add additional CPU overhead. That’s why you should use the ASM file system, which is designed to avoid this problem. By using ASM, your database is stored on multiple disk spindles instead of one. It will also avoid wasting space on redundant backups of your database.
To create a guaranteed restore point, you must monitor the flash recovery area space. You can manage this space by setting a retention policy and deleting transient files. You should also increase the disk space available to the flash recovery area. Using a retention policy for the flash recovery area space is a safe and reliable way to control how files are deleted. The flash recovery area space can be filled up quickly if you use a backup retention policy.
RMAN can automatically create control file autobackups in the flash recovery area if it does not have another destination. For example, when you use a disk backup, RMAN will create a file in the flash recovery area if you don’t configure any other destination. The other option is to configure the retention policy for the backup. You can configure the retention policy by setting the LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n explicitly or implicitly in RMAN.
Delete system archived logs from the flash recovery area
You may be wondering how to delete system archived logs from the flash recovery zone. The first step is to back up your database. When this is done, archived logs are deleted from the flash recovery area. The flash recovery zone is a special storage location for archived redo logs. The database stores these logs in separate locations. This area is often larger than the database’s normal disk space.
Depending on the size of your system, it may be impossible to back up all the files in the flash recovery zone. To solve this problem, you can backup the files in the flash recovery zone to a tape or media manager. Before doing this, you must make sure that the SYSTEM tablespace block size is larger than the control file block size. Otherwise, you’ll lose the records for tape backups. You should also choose a larger block size, like 32 KB.
If you need to back up archive logs, you can perform a BACKUPRECOVERYAREA operation. The BACKUPRECOVERYAREA command backs up all files in the recovery area to tape. However, the BACKUPRECOVERYAREA command doesn’t back up flashback logs. To delete a file in the flash recovery area, you need to specify the location of the backup files by using DELETE.
If you want to keep your archived redo logs for as long as possible, you need to balance the number of backups in the flash recovery area with the amount of disk space you’re using. If your system requires more space, then you can delete the backup logs on disk or tape. This will free up more space in your fast recovery area. If you have a large production database, this is an essential part of data backups.
If your flash recovery area has not enough reclaimable space, Oracle will continue to archive the files. However, this could result in a database hang. If you have a low-end server, you should consider deleting nonessential files in order to free up disk space in the flash recovery area. Once this has been done, you can retry the archiving process periodically until the area is free.
This option is useful if you’re using RMAN frequently to back up your database. RMAN will automatically create backup pieces and image copies of the flash recovery area. But, it can also delete system archived logs. If you don’t want to use the flash recovery area, you can manually delete the files from the flash recovery area. It will then be unable to recover the space and the error will occur.
About The Author

Mindy Vu is a part time shoe model and professional mum. She loves to cook and has been proclaimed the best cook in the world by her friends and family. She adores her pet dog Twinkie, and is happily married to her books.